Introduction
In the modern digital era, where secure data, scalable solutions, and seamless connectivity are crucial, AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) has become an essential tool for businesses across the globe. In this blog, we will explore more about VPC, its benefits, components, and more.
What is AWS VPC ?
VPC stands for Virtual Private Cloud, and it is a fundamental component of cloud computing infrastructure provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) . A VPC allows users to create a logically isolated section of the cloud where they can deploy and run their virtual machines, applications, and other resources.
Benefits of AWS VPC
- Better Security: In AWS VPC, Network Access Control Lists (NACLs) and Security Groups (SGs) act as virtual firewalls, controlling inbound and outbound traffic at the instance and subnet levels. This helps protect data from security threats.
- Cost Efficiency: With AWS VPC, costs can be optimized by only paying for what you use.
- Controlled Environment: VPC lets you create your own private space in the AWS cloud, like having your own virtual network.
- Connectivity Options: AWS offers a variety of connectivity options, such as AWS Direct Connect and VPN connections, which enable users to establish secure connections between their on-premises infrastructure and AWS cloud resources.
- Easy Scaling: In VPC, users can simply add more resources without causing any disruption as their business grows.
Components of AWS VPC
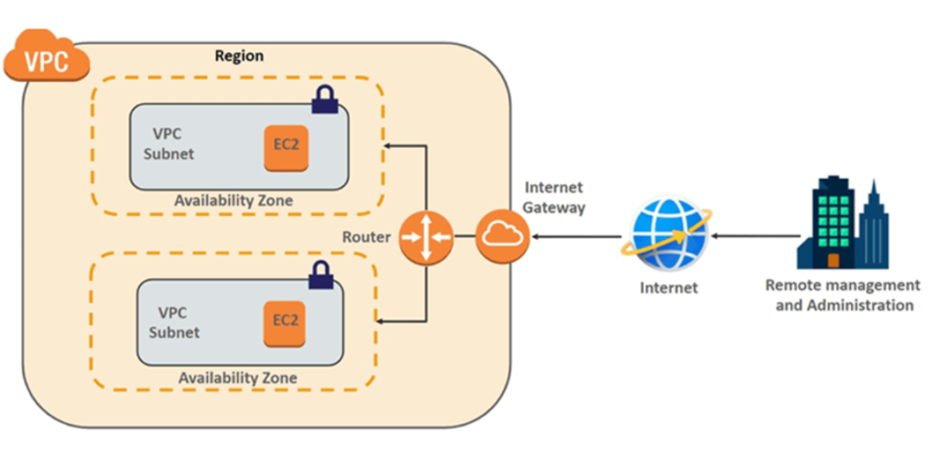
- Subnets: VPCs are divided into subnets, which are smaller IP address ranges within the overall VPC IP address range. Subnets help in organizing and segmenting resources based on different criteria.
- Security Groups and Network Access Control Lists (NACLs): These are used to control inbound and outbound traffic to and from instances in the VPC. Security Groups are stateful and operate at the instance level, while NACLs are stateless and operate at the subnet level.
- Internet Gateway: A VPC can be connected to the internet using an Internet Gateway, allowing instances within the VPC to communicate with the internet and vice versa.
- Route Tables: These tables define the rules for routing traffic within the VPC and between the VPC and external networks.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) and Direct Connect: These are options for connecting a VPC to an on-premises data center securely.
- Elastic IP Addresses: These are static IP addresses that can be associated with instances in the VPC, providing a consistent endpoint for communication.
- Peering: VPC peering allows the connection of two VPCs, enabling them to communicate with each other using private IP addresses.
- VPC Endpoints: These allow instances in the VPC to connect to AWS services (such as S3) without traversing the public internet.
- AWS Transit Gateway: It simplifies the network architecture and allows for interconnecting multiple VPCs and on-premises networks.
Use Cases of AWS VPC
The uses cases of AWS VPC are :
- Web Application Hosting
- Data Analytics
- Hybrid Cloud Deployment
- Disaster Recovery
- Internet of Things (IoT)
Conclusion
AWS VPC offers a range of benefits, including Better Security, Cost Efficiency, Controlled Environment, Connectivity Options, Easy Scaling. By leveraging these benefits, organizations can build secure, scalable, and highly available cloud infrastructures that support their business objectives and enable innovation and growth.
Also read our blog post on Elastic Load Balancing.
What’s Next ?
“We’re here to support you! Should you have any questions or need assistance, don’t hesitate to get in touch with us. Contact us at info@uranuscloudsolutions.com and we’ll be happy to help. Your satisfaction is our priority!”.